The key differences between Japanese power plugs and other global standards include:
Plug Shape and Size: Japanese power plugs typically have two flat pins in parallel, sometimes with a ground pin, while other global standards may feature different plug shapes and sizes such as round pins or angled prongs.
Voltage and Frequency: Japan operates on a 100-volt electrical system with a frequency of 50 or 60 Hertz, whereas other countries may use different voltages (e.g., 110V, 220V, 240V) and frequencies (e.g., 50Hz, 60Hz).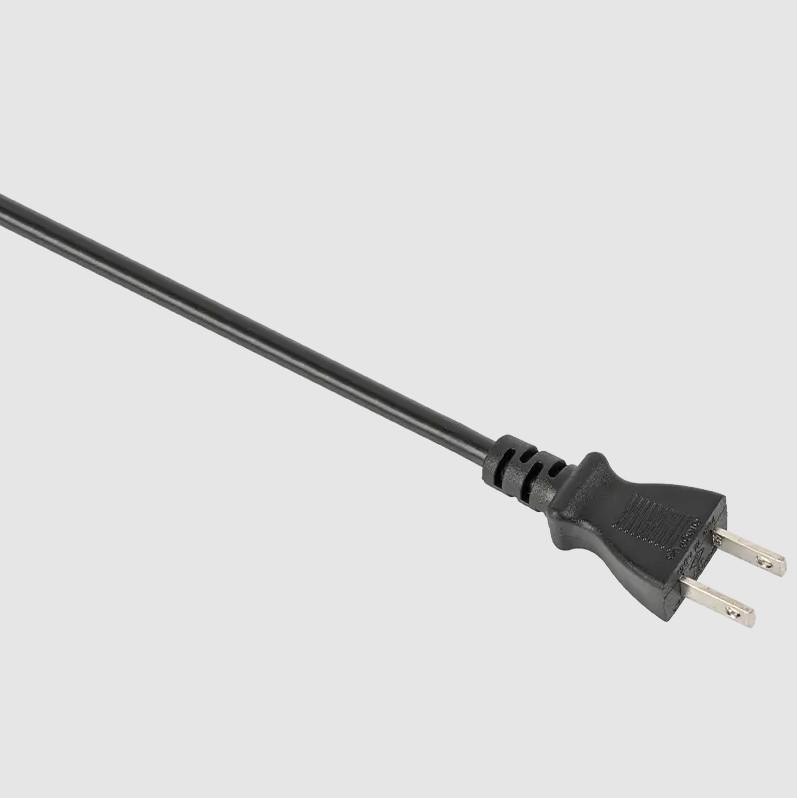
Socket Design: Japanese power sockets are often recessed into walls with the pins deeply set, unlike some other countries where sockets may be surface-mounted or have different configurations.
Grounding: While grounding is common in many countries, not all Japanese power plugs include a ground pin, depending on the appliance and the specific plug type used.
Compatibility: Due to these differences, Japanese power plugs may not be directly compatible with power outlets in other countries without the use of adapters or voltage converters.
Safety Standards: Japanese power plugs adhere to the safety standards set by the Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS), which may have variations from standards such as those set by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) or other regional standards bodies.
Polarity: The orientation of the pins in Japanese power plugs may differ from other standards, impacting the polarity of the electrical connection.
Understanding these differences is crucial for travelers, expatriates, and businesses operating internationally to ensure compatibility and safety when using electrical appliances across different regions.
2023.03.23
2023.03.23
2023.03.23
2023.03.23
Tel:0086-574 - 62162855
E-mail:[email protected]
Address:NO.20, Changzhen Road, Sibei Village, Simen Town, Yuyao City, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China 315472
